Blog:Why You Need to See a Houston Diabetic Eye Specialist Before Year-End
Diabetes can damage retinal blood vessels long before vision changes are noticed. Scheduling a diabetic eye exam in Houston before year-end is a crucial preventive step to preserve sight. This article covers annual dilated eye exams, diabetic retinopathy development, comprehensive exam expectations with advanced imaging, and effective treatments and lifestyle steps. Early detection is vital, as silent early disease often leads to delayed screening, missing interventions that prevent irreversible vision loss.
Why Is an Annual Diabetic Eye Exam Crucial for Houston Patients with Diabetes?
An annual diabetic eye exam detects retinal changes caused by high blood sugar before symptoms appear, enabling interventions that prevent vision loss. Elevated glucose damages retinal vessels, causing microaneurysms, hemorrhages, and fluid accumulation, identifiable through imaging and dilated exams. Early detection prevents progression to sight-threatening stages, establishing a baseline for tracking disease and coordinating systemic risk management with primary care. As early disease is often asymptomatic, annual exams are vital for timely intervention and optimal outcomes.
Importantly, patients diagnosed as pre-diabetic should also receive regular comprehensive eye exams. Even before full diabetes develops, fluctuating blood sugar can temporarily alter vision and begin affecting small retinal vessels. Early monitoring helps detect subtle changes, reinforces preventive health habits, and ensures prompt intervention if the condition progresses.
The Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS) has established criteria for performing dilated eye examinations in patients with diabetes, underscoring their importance in preventing diabetes-related blindness.
Annual Eye Exams Crucial for Preventing Diabetes-Related Blindness
Diabetes mellitus remains the leading cause of new cases of blindness among US adults. Routine dilated eye examinations can facilitate early detection and intervention for diabetes-related eye disease, providing an opportunity to reduce the risk for diabetes-related blindness in working-aged Americans. The Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS) established criteria for performing dilated eye examination in patients with diabetes.
Evaluating adherence to dilated eye examination recommendations among patients with diabetes, combined with patient and provider perspectives, 2016
What Are the Silent Symptoms of Diabetic Eye Disease?
Diabetic eye disease often begins without noticeable symptoms, making screening essential even with normal vision. Early signs, if present, may include intermittent blurred vision, new floaters, difficulty reading, or subtle color changes, often dismissed as fatigue. These mild, intermittent symptoms are frequently missed until advanced disease causes persistent vision loss, underscoring the importance of annual dilated eye exams. Imaging and dilation are emphasized to uncover hidden retinal damage.
How Does Early Detection Prevent Vision Loss from Diabetic Retinopathy?
Early detection prevents vision loss by identifying retinal changes when monitoring, medical therapy, or focal procedures can halt or reverse damage. Detecting microaneurysms or macular swelling via OCT allows targeted anti-VEGF therapy or focal laser to reduce edema and preserve central vision. Recognizing progressive ischemia can lead to panretinal laser or specialist referral before complications. Timely detection also facilitates coordination with primary care to improve glycemic and blood pressure control, slowing retinal damage. Early screening preserves more vision and reduces the need for complex surgery, as treatment is most effective in earlier stages.
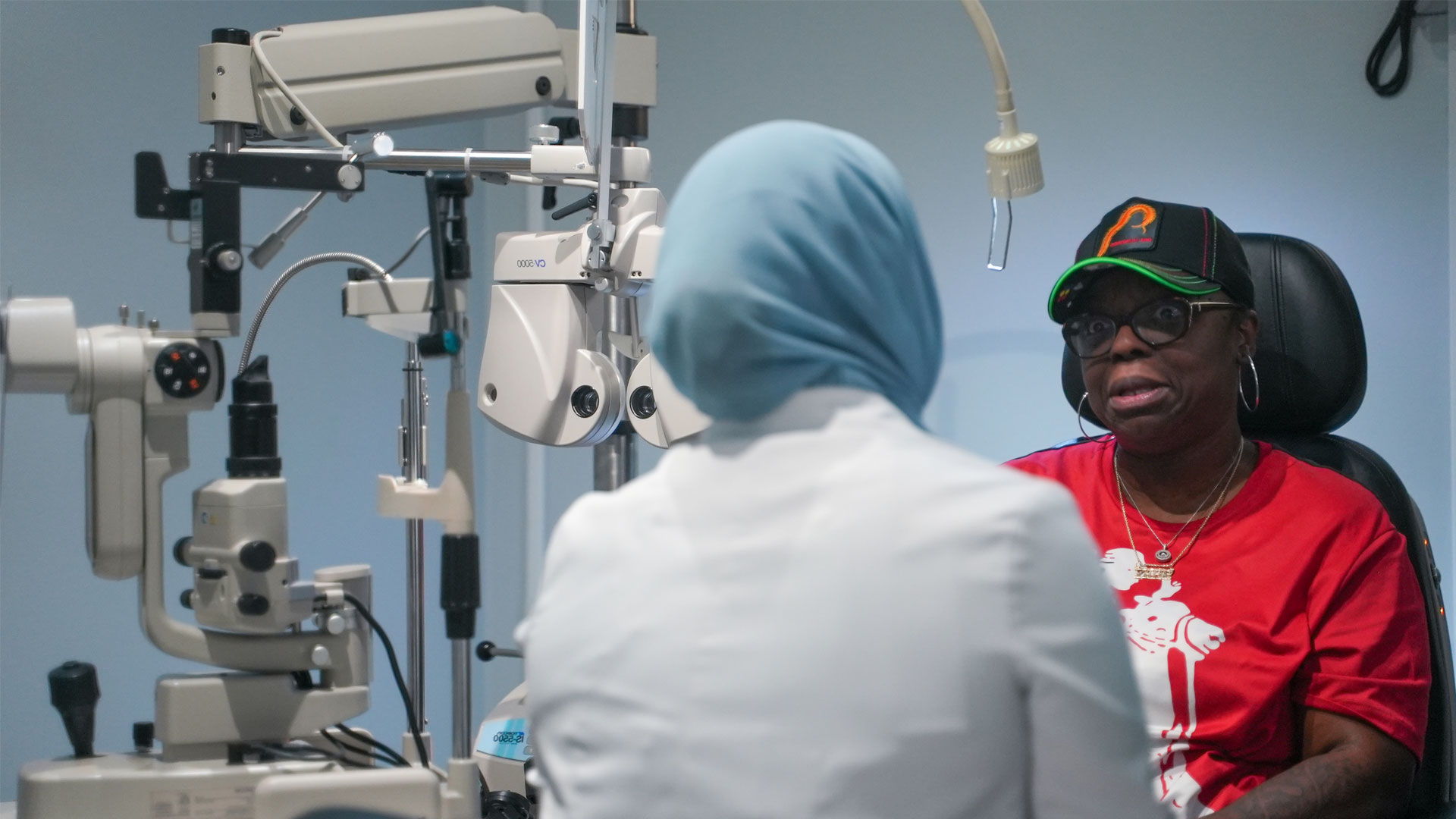
What Happens During a Comprehensive Diabetic Eye Exam at Texas State Optical Champions?
A comprehensive diabetic eye exam includes reviewing medical history, measuring visual acuity and eye pressure, dilating pupils, and capturing advanced retinal images like OCT and ultra-widefield imaging. This structured exam combines clinical evaluation with diagnostic imaging to map the retina, quantify macular edema, and establish a baseline. Patients receive clear communication about findings, individualized follow-up plans, and treatment or referral recommendations, aiding patient preparation and diagnostic accuracy.
Which Advanced Diagnostic Technologies Are Used for Diabetic Eye Exams?
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and ultra-widefield retinal cameras (OPTOS) are essential diagnostic tools. OCT provides high-resolution cross-sectional images of the macula, quantifying fluid and thickness changes crucial for early detection and monitoring of diabetic macular edema. Ultra-widefield imaging captures the peripheral retina, revealing ischemic lesions that guide panretinal treatments. These technologies, combined with a dilated fundus exam, offer comprehensive retinal assessment, enabling precise disease staging and targeted management.
| Step | Purpose | What the Patient Experiences |
|---|---|---|
| Medical history and symptom review | Identify systemic risk factors and vision changes | Short questionnaire and discussion with the clinician |
| Visual acuity and intraocular pressure | Assess baseline vision and glaucoma risk | Reading letters and a brief tonometry check |
| Pupil dilation and dilated retinal exam | Enable full view of the retina and optic nerve | Eye drops producing temporary light sensitivity and blur |
| OCT imaging | Detect macular edema and retinal thickness changes | Comfortable, noninvasive scan that takes seconds per eye |
| Ultra-widefield (Optos) imaging | Reveal peripheral retinal changes and ischemia | Quick photographic capture without contact |
This table clarifies each component's contribution to a complete evaluation and sets patient expectations.
Bring a current list of medications, recent HbA1c value if available, and any notes from your primary care provider.
Expect pupil dilation that may blur near vision for several hours; plan transportation accordingly.
Bring current eyeglasses or contact lens information and your insurance card or plan details.
Preparing these items streamlines the visit, improves diagnostic value, and supports coordinated care.
How Does Diabetic Retinopathy Develop and What Are Its Stages?
Diabetic retinopathy results from chronically high blood glucose damaging retinal microvessels, leading to leakage, ischemia, and abnormal new vessel growth. Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) begins with microvascular leakage and microaneurysms. Progressive capillary closure then leads to ischemia, neovascularization, and proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), carrying a higher risk of hemorrhage and retinal detachment. Diabetic macular edema (DME), causing central vision loss from fluid accumulation, can occur at any stage. Understanding these stages guides monitoring and therapy to prevent severe vision loss.
What Are the Key Symptoms and Risks of Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy symptoms vary by stage, including intermittent blurred vision, floaters, central vision distortion, or sudden vision loss; early stages are often asymptomatic. Risk factors accelerating progression include long diabetes duration, poor glycemic control (high HbA1c), uncontrolled blood pressure, high cholesterol, and pregnancy. Recognizing modifiable risks, like improving HbA1c and blood pressure, supports targeted interventions and slows progression. Symptom awareness prompts earlier re-evaluation.
Research indicates that diabetes duration, dyslipidemia, and microalbuminuria are significant risk factors for the development and progression of diabetic retinopathy, emphasizing the need for early detection.
Key Risk Factors for Diabetic Retinopathy Progression
Diabetes duration, dyslipidemia, and microalbuminuria are the major risk factors for the development and progression of diabetic retinopathy. Early detection of diabetic retinopathy at an early stage is crucial.
Clinical predictors of diabetic retinopathy progression; a systematic review, AHA Ghamdi, 2020
What Are the Differences Between Non-Proliferative and Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy?
Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) features microaneurysms, hemorrhages, and hard exudates, often managed with observation and systemic control. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) involves neovascularization—fragile new blood vessels prone to bleeding and tractional detachments—requiring aggressive treatments like panretinal laser or surgical referral. Diabetic macular edema (DME) can occur in either stage, prompting anti-VEGF injections or focal laser when vision is affected. Differentiating NPDR and PDR guides monitoring frequency and treatment escalation.
What Treatment Options Are Available for Diabetic Eye Disease in Houston?
Diabetic eye disease treatment ranges from observation and medical therapies to laser procedures and surgery, based on disease stage, diabetic macular edema presence, and treatment response. Intravitreal anti-VEGF injections treat diabetic macular edema and reduce abnormal vessel growth, often stabilizing vision with repeated doses. Laser photocoagulation (focal/grid for macular leaks, panretinal for widespread ischemia) reduces severe vision loss risk by sealing vessels and decreasing metabolic demand. Vitrectomy surgery is reserved for complications like non-clearing vitreous hemorrhage or tractional retinal detachment, typically after less-invasive therapies fail.
| Treatment | Mechanism | Typical Use / Recovery |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-VEGF injections | Inhibit VEGF to reduce edema and neovascular growth | Used for DME and some PDR cases; repeated treatments and monitoring required |
| Focal/Grid Laser | Seals leaking microaneurysms and diminishes macular edema | Applied when localized leakage is present; outpatient procedure, minimal recovery |
| Panretinal Photocoagulation (PRP) | Ablates ischemic peripheral retina to reduce neovascular stimulus | Used for PDR to lower bleeding risk; may affect peripheral vision temporarily |
| Vitrectomy Surgery | Removes blood and relieves tractional forces on retina | Reserved for non-clearing hemorrhage or tractional detachment; recovery includes positioning and follow-up care |
This table clarifies each option's function and when a specialist might recommend escalation.
How Do Laser Therapy and Injections Help Manage Diabetic Retinopathy?
Laser therapy and intravitreal injections manage retinal disease through distinct mechanisms. Laser photocoagulation reduces oxygen demand in ischemic retina, decreasing abnormal vessel growth. Anti-VEGF injections block vascular endothelial growth factor, reducing macular edema and stopping neovascular proliferation. Laser is used for proliferative disease or focal leaks, while injections directly improve central macular thickness and vision with edema. Treatment often combines both, adjusted based on individual response and regular OCT/retinal photography findings. Texas State Optical Champions provides high-quality imaging and coordinates referrals to retinal specialists.
When Is Surgery Recommended for Diabetic Eye Conditions?
Surgery, typically vitrectomy, is recommended when non-surgical treatments fail to resolve complications like persistent vitreous hemorrhage, tractional retinal detachment, or dense scar tissue threatening central vision. The procedure removes hemorrhage and scar tissue, relieves retinal traction, and may involve membrane peeling or gas/air tamponade for reattachment. Recovery includes close follow-up and visual rehabilitation. Surgical referral is coordinated by the eye care team when less invasive options are unlikely to preserve vision. Timely detection and early treatment often reduce the need for surgery.
How Can You Protect Your Vision Beyond the Exam?
Protecting vision involves active management of systemic risk factors, lifestyle modifications, timely follow-up, and prompt reporting of visual changes. Optimal blood sugar (HbA1c), blood pressure, and cholesterol control slow microvascular damage and disease progression. Smoking cessation and regular physical activity improve vascular health. Adherence to medications and routine retinal imaging enables early intervention. Coordinating care with primary care or endocrinology ensures ocular recommendations align with systemic treatment plans, crucial for long-term sight preservation.
| Factor | Impact on Retina | Recommended Action / Target |
|---|---|---|
| High blood sugar | Accelerates microvascular damage and leakage | Aim for individualized HbA1c targets and regular monitoring with PCP |
| High blood pressure | Increases risk of hemorrhages and ischemia | Control BP through lifestyle and meds per PCP guidance |
| Elevated cholesterol | Contributes to vascular dysfunction | Manage lipids with diet and medication when indicated |
| Smoking | Worsens vascular health and healing | Quit smoking to improve microvascular outcomes |
This table clarifies how systemic control reduces retinal risk and supports discussions with primary care providers.
Follow a balanced diet and exercise routine to support stable blood glucose and vascular health.
Adhere to prescribed diabetes and blood pressure medications and track lab values regularly.
Stop smoking and limit alcohol intake to reduce vascular inflammation and improve healing.
These actionable changes lower long-term progression risk and enhance eye treatment effectiveness.
How to Find and Schedule an Appointment with a Houston Diabetic Eye Specialist Before Year-End?
To schedule an appointment, verify insurance coverage, prepare medical records, and book a dilated exam before year-end. Early booking is beneficial for utilizing remaining benefits or meeting calendar-year screening intervals. When choosing a provider, prioritize those offering comprehensive diabetic eye exams with OCT and widefield imaging, and inquire about follow-up intervals based on your diabetes type and control.
Verify insurance coverage and preferred provider status with your plan to understand benefits and any referral requirements.
Gather recent lab results (HbA1c), medication lists, and a short summary of diabetes history to submit or bring to the appointment.
Schedule early in the day if possible, allow time for dilation, and arrange transportation when pupil dilation is expected.
These steps reduce administrative delays and ensure a productive visit.
What Makes Texas State Optical Champions the Trusted Choice for Diabetic Eye Care in Houston?
Texas State Optical Champions provides comprehensive medical and diabetic eye exams utilizing advanced diagnostic technology like OCT and Optos for retinal health evaluation and diabetic macular edema detection. Serving local communities, experienced eye doctors, including Dr. Ayesha Butt, offer patient-centered care emphasizing clear communication and coordinated management with primary care. This ensures accurate diagnosis and timely referrals for specialized retinal treatment, making it a practical local choice for thorough diabetic eye care.
Ultra-widefield fundus imaging is a valuable tool that captures a significantly larger portion of the retina compared to traditional methods, aiding in the early detection and management of diabetic retinopathy.
Ultra-Widefield Imaging for Early Diabetic Retinopathy Detection
Early detection and treatment are important for preventing vision loss from diabetic retinopathy. Historically, the gold standard for grading diabetic retinopathy has been based on 7-field 30-degree color fundus photographs that capture roughly the central third of the retina. Our aim was to review recent literature on the role of ultra-widefield (allowing capture of up to 82% of the retina in one frame) fundus imaging in screening, prognostication, and treatment of diabetic retinopathy.
The role of ultra-widefield fundus imaging and fluorescein angiography in diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy, TYA Liu, 2021
How Can You Book Your Annual Diabetic Eye Exam Today?
To book your annual diabetic eye exam before year-end, prepare your medication list and recent lab values, confirm insurance, and contact a local provider for a dilated diabetic eye exam. Specify that you need diabetic retinal imaging (OCT and ultra-widefield) to ensure proper appointment allocation. Bring identification, medication lists, and recent HbA1c results to maximize visit efficiency and clinical value. Early booking ensures timely screening and prevents missing crucial, vision-preserving care.